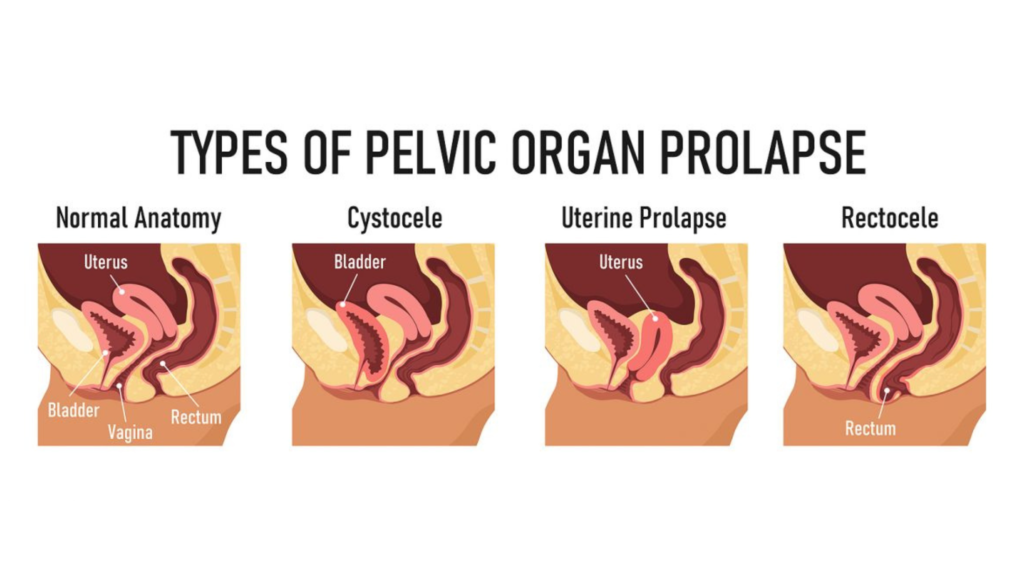
In the intricate tapestry of women’s health, the connection between pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and sexual dysfunction is a crucial yet often overlooked thread. Pelvic organ prolapse, a condition affecting many women worldwide, not only poses physical challenges but can also significantly impact one’s sexual well-being. In this blog, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the dynamic relationship between pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction, unravelling the complexities that intertwine these two aspects of women’s health.
As we delve into this subject, it becomes apparent that the effects of pelvic organ prolapse extend far beyond the anatomical realm. This condition, characterized by the descent of pelvic organs like the bladder, uterus, or rectum into the vaginal canal, brings with it a spectrum of physical sensations and emotional nuances that inevitably influence intimate aspects of life.
Join us on this journey of understanding as we unravel the multifaceted layers that bind pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction, exploring the challenges faced by individuals and the avenues available for addressing these concerns. By shedding light on this important connection, we aim to empower individuals and healthcare professionals alike to navigate this intersection with compassion, knowledge, and a commitment to holistic well-being.
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a condition where pelvic organs like the bladder, uterus, or rectum descend into the vaginal canal due to weakened pelvic floor muscles and tissues. Common in women, especially after childbirth and with age, POP can cause symptoms like pelvic pressure and urinary issues. Risk factors include multiple childbirths, ageing, and conditions that strain the pelvic floor. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes and pelvic floor exercises to surgical interventions, aiming to alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Early recognition and proper management are crucial for addressing this often-overlooked aspect of women’s health.
The Impact of Pelvic Organ Prolapse on Sexual Function
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) can have a significant impact on sexual function, influencing both physical and psychological aspects of intimate relationships. Let’s delve into the details of how POP affects sexual well-being.
Physical Discomfort
- Pain during Intercourse
One of the primary physical impacts of POP on sexual function is pain or discomfort. The descent of pelvic organs into the vaginal canal can lead to pressure and stretching, causing pain and making sexual activity less enjoyable.
- Changes in Sensation
The displacement of pelvic organs may alter the usual sensation during sex. Women with POP might experience a decrease in vaginal tightness, lubrication, or overall sensitivity, affecting arousal and satisfaction.
Psychological Impact
- Body Image and Self-Esteem
The physical changes associated with pelvic organ prolapse can have a profound psychological impact on a woman’s body image and self-esteem. The visible bulge or discomfort may lead to feelings of self-consciousness and impact the willingness to engage in sexual activities.
- Anxiety and Depression
Living with POP can contribute to anxiety and depression, which can further exacerbate sexual dysfunction. Concerns about pain, appearance, or fear of causing harm during intercourse may contribute to heightened stress levels.
Communication Challenges
- Difficulty Expressing Concerns
- Coping with the physical and emotional aspects of pelvic organ prolapse may make it challenging for individuals to openly communicate their concerns with their partners. This lack of communication can strain the overall intimacy in the relationship.
- Impact on Relationship Dynamics
- The changes in sexual function may lead to shifts in relationship dynamics. Partners may struggle to understand the physical limitations and emotional toll of POP, which can affect overall relationship satisfaction.
Addressing Sexual Dysfunction in Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Addressing sexual dysfunction in the context of pelvic organ prolapse (POP) involves a multi-faceted approach that combines medical intervention, pelvic floor rehabilitation, psychosocial support, and education. Below, we’ll explore in detail how each aspect plays a crucial role in managing sexual dysfunction associated with POP:
1. Medical Intervention
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
- Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals, including gynaecologists or urogynecologists, is the first step.
- Comprehensive evaluations help determine the severity of POP and its specific impact on sexual function.
Treatment Options
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Healthcare providers may recommend pelvic floor exercises (Kegels) to strengthen the muscles supporting the pelvic organs.
- Pessaries: These devices can provide structural support to the prolapsed organs and alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe prolapse, surgical procedures may be considered to repair and restore the pelvic floor.
2. Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Specialized Exercises
- Physical therapists with expertise in pelvic health can design personalized exercise programs.
- Exercises focus on strengthening pelvic floor muscles, improving muscle tone, and enhancing overall pelvic health.
Biofeedback and Electrical Stimulation
- Biofeedback techniques and electrical stimulation may be incorporated to ensure proper muscle engagement and enhance the effectiveness of exercises.
3. Psychosocial Support
Counselling
- Individuals and couples may benefit from counselling to address the emotional impact of POP on sexual function.
- Discussing concerns, fears, and expectations in a therapeutic setting can foster understanding and resilience.
Support Groups
- Participating in support groups, either in-person or online, allows individuals to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Connecting with others facing similar challenges can reduce feelings of isolation.
4. Intimacy Education
Communication Strategies
- Educating individuals and couples on effective communication is vital for navigating the changes brought about by POP.
- Encouraging open and honest discussions about sexual desires, concerns, and preferences fosters a supportive environment.
Alternative Sexual Positions
- Healthcare providers can offer guidance on alternative sexual positions that minimize discomfort associated with POP.
- Experimenting with positions can help individuals find what works best for them.
Lubrication and Comfort Measures
- Recommending the use of water-based or silicone-based lubricants can ease discomfort during intercourse.
- Comfort measures, such as using pillows or cushions for support, may be suggested.
5. Continued Follow-Up
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals allow for the monitoring of treatment effectiveness.
- Treatment plans can be adjusted based on the individual’s progress and evolving needs.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored the challenges posed by POP, it’s essential to emphasize that effective management is not only possible but also integral to restoring a sense of normalcy and quality of life. Seeking medical guidance, engaging in pelvic floor rehabilitation, embracing psychosocial support, and educating oneself about intimacy in the context of POP are vital components of this journey.
Remember, addressing sexual dysfunction associated with pelvic organ prolapse is not a solitary endeavour. It involves a partnership between individuals, healthcare professionals, and support networks. By fostering open communication, seeking appropriate interventions, and embracing a patient-centred approach, individuals can reclaim control over their sexual health and rediscover the joy of intimate connections.
In this ongoing exploration of women’s health, let us continue to break down stigmas, promote awareness, and empower individuals to prioritize their well-being. The journey to understanding and managing the connection between pelvic organ prolapse and sexual dysfunction is one of resilience, self-discovery, and ultimately, reclaiming a fulfilling and satisfying intimate life.
Dr. Sumit Sharma is an experienced urologist, andrologist, and kidney transplant surgeon with over 20 years of clinical experience. He is the founder of the Department of Urology at multiple hospitals in Gurgaon and has established successful kidney transplant programs across the city.
With a commitment to the highest standards, Dr. Sumit Sharma ensures personalised, professional treatment, making your well-being the primary focus. Choose Dr. Sumit Sharma for outstanding Urological care in Gurgaon.